In DrCAF, we try to make it more powerful and convenient to be used. This USAGE is prepared for the online service. The DrCAF provides the browse and search options. Thus, users can easily acess the gene page through the above two ways.
1. Browse. Two simple ways have been provided for users to browse CAF-associated proteins in database.
(1) Browse Cancer type. You can click one of these cancer types to unfold all caf types in this cancer type and browse all proteins of corresponding cancer type.
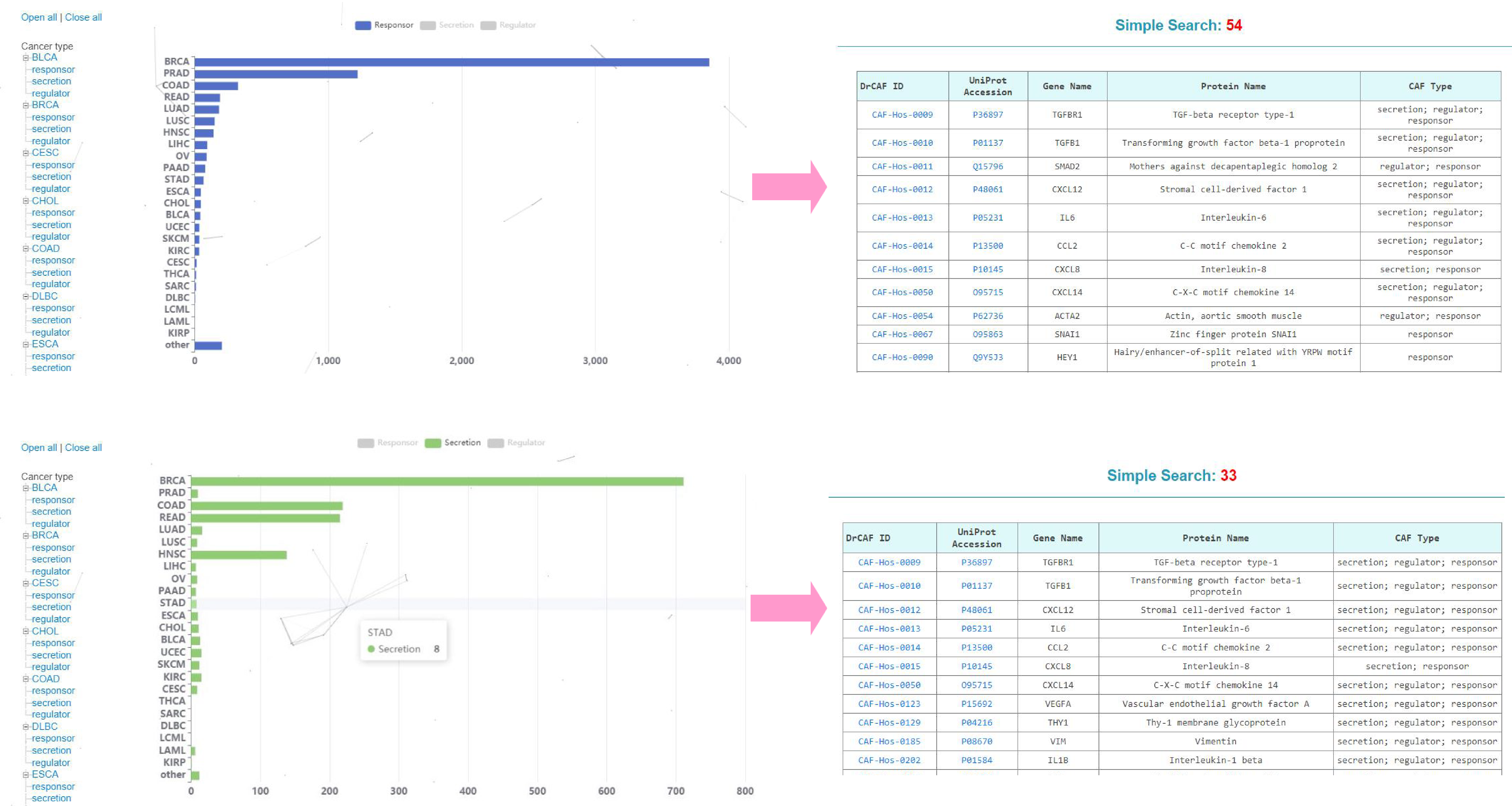
(2) Browse by CAF types: You can select one of the three types to obtain all proteins of corresponding type.
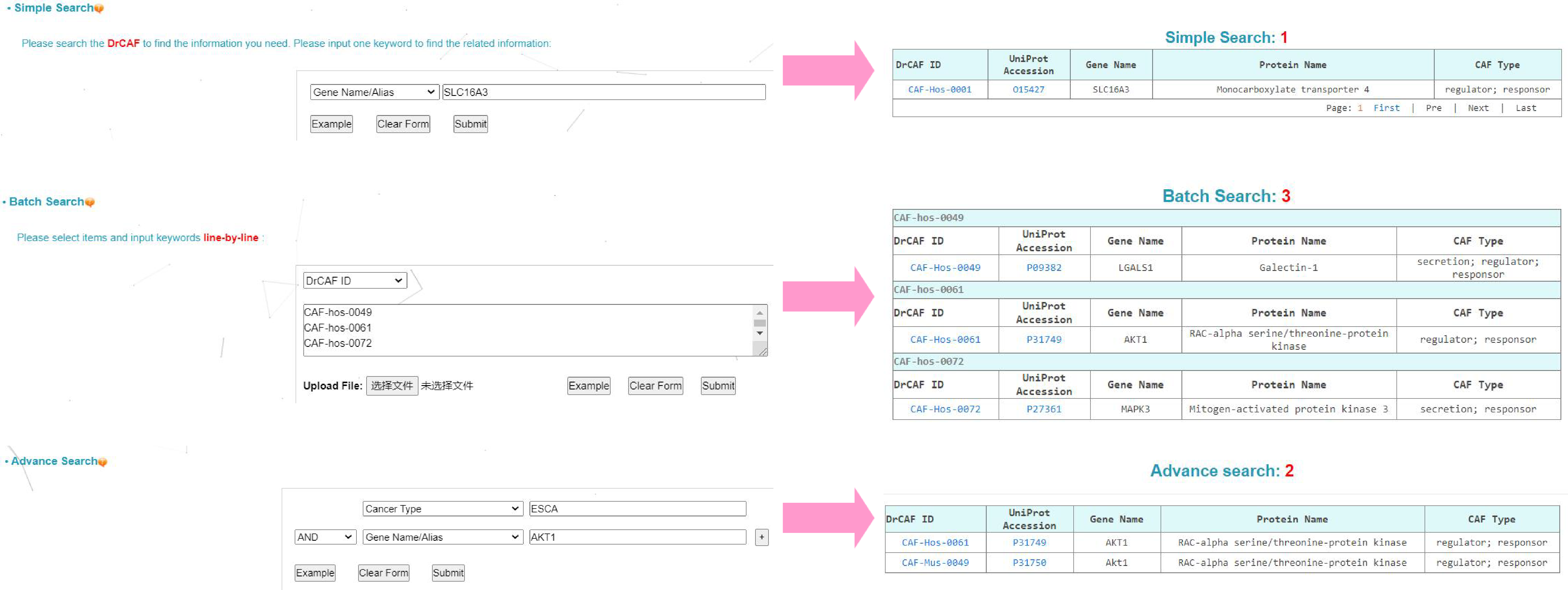
2. Search. Three search options are provided, including simple search,batch search and advance search.
(1) Simple search. You can input one keyword to search the DrCAF. The search fields include DrCAF ID, UniProt Accession, Protein Name and Gene Name/Alias.
EXAMPLE: You can click on the "Example" button to load an instance. All species containing FUS will be shown by clicking on the "Submit" button.
(2) Batch search. You can input one keyword to search several the DrCAF. The search fields include DrCAF ID, UniProt Accession, Protein Name and Gene Name/Alias.
EXAMPLE: You can click on the "Example" button to load an instance. All species containing Ensembl Gene ID like "CAF-hos-0049; CAF-hos-0061; CAF-hos-0072" will be shown by clicking on the "Submit" button.
(3) Advance search. allows you to input up to three terms to find the information more specifically. The querying fields can be empty if less terms are needed. The three terms could be connected by the following operators:
exclude: If selected, the term following this operator must be not contained in the specified field(s)
and: the term following this operator has to be included in the specified field(s)
or: either the preceding or the following term to this operator should occur in the specified field(s)
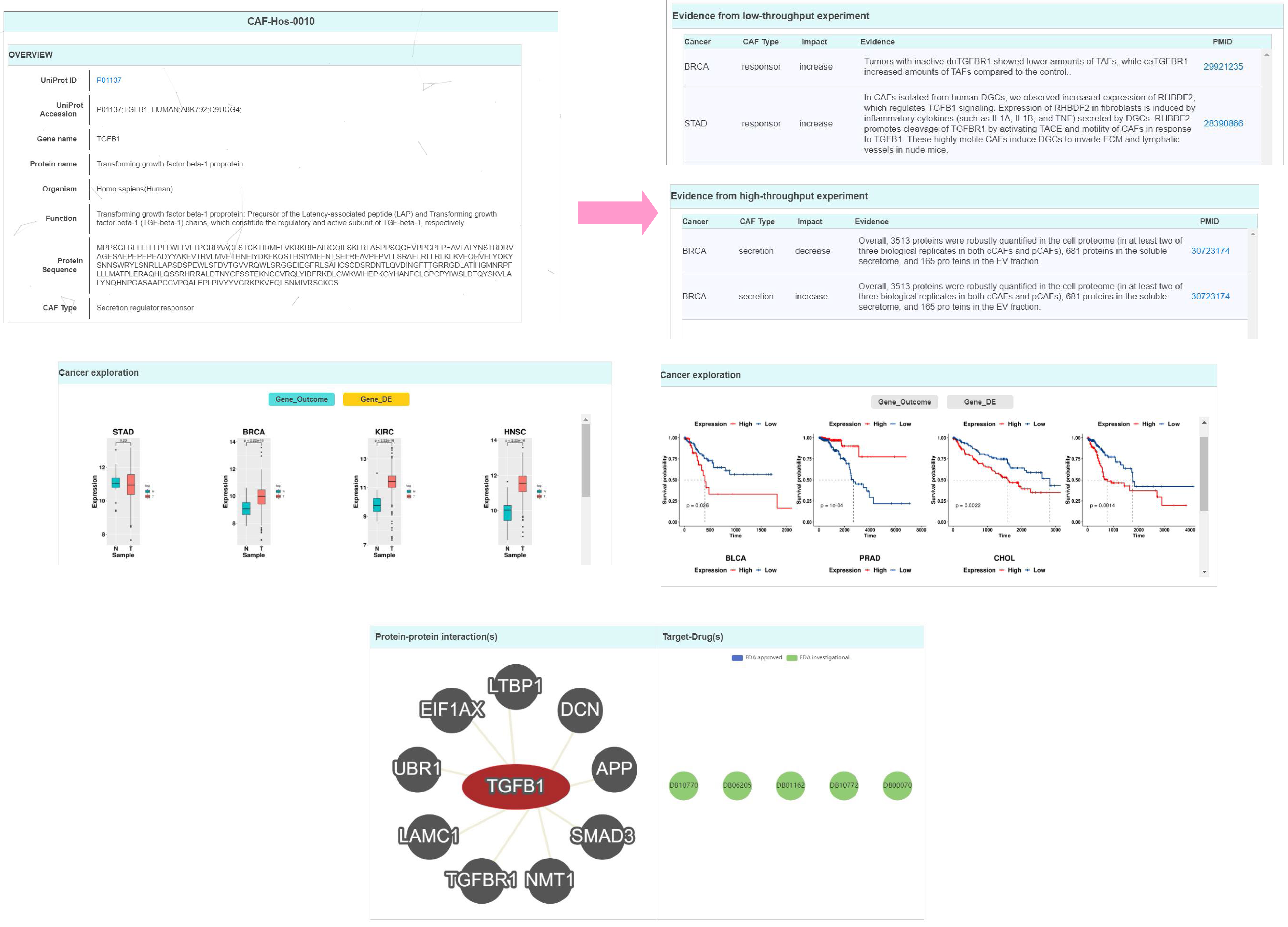
3. Gene page. More specific information for the gene is displayed here which includes basic and additional annotations.
(1) Basic annotations. This part shows the basic information for a gene that covered 3 modules, including “Overview”, “Evidence from low-throughput experiment” and “Evidence from low-throughput experiment” information. Users can click each module to view the corresponding information. (2) Additional annotations. This part shows the rich annotations for a gene which was extracted by compiling and integrating the knowledge that covered 3 aspects, including “Cancer exploration”, “Protein-protein interaction(s)” and “Target-Drug(s)” molecular interactions from 5 widely used databases. Users can click one of sources and view the details of the gene in the database.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Q: What is the difference between "low-throughput" and "high-throughput" evidence?
A: The protein is annotated as low-throughput or high-throughput according to the methods it has been reported by the paper. For example, if a protein is clearly reported that it is a CAF-associated protein, we will mark it as "low-throughput evidence". If a protein is found only by proteomics but without experiment’s identification, we will annotate it as "high-throughput evidence".
2. Q: I have a few questions which are not listed above, how can I contact the authors of DrCAF?
A: Please contact the the major authors: Dr. Yaping Guo for details.